TSMC Details 3nm N3, 5nm N5, and 3DFabric Technology
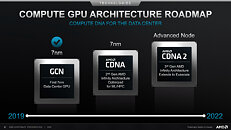
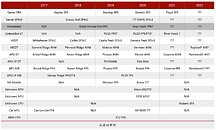
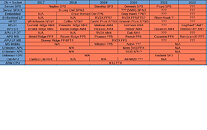
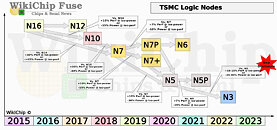
TSMC on Monday kicked off a virtual tech symposium, where it announced its new 12 nm N12e node for IoT edge devices, announced the new 3DFabric Technology, and detailed progress on its upcoming 5 nm N5 and 3 nm N3 silicon fabrication nodes. The company maintains that the N5 (5 nm) node offers the benefits of a full node uplift over its current-gen N7 (7 nm), which recently clocked over 1 billion chips shipped. The N5 node incorporates EUV lithography more extensively than N6/N7+, and in comparison to N7 offers 30% better power at the same performance, 15% more performance at the same power, and an 80% increase in logic density. The company has commenced high-volume manufacturing on this node.
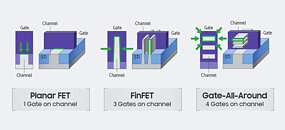
2021 will see the introduction and ramp-up of the N5P node, an enhancement of the 5 nm N5 node, offering a 10% improvement in power at the same performance, or 5% increase in performance at the same power. A nodelet of the N5 family of nodes, called N4, could see risk production in Q4 2021. The N4 node is advertised as "4 nm," although the company didn't get into its iso-power/iso-performance specifics over the N5 node. The next major node for TSMC will be the 3 nm N3 node, with massive 25%-30% improvement in power at the same performance, or 10%-15% improvement in performance at same power, compared to N5. It also offers a 70% logic density gain over N5. 3DFabric technology is a new umbrella term for TSMC's CoWoS (chip on wafer on substrate), CoW (chip on wafer), and WoW (wafer on wafer) 3-D packaging innovations, with which it plans to offer packaging innovations that compete with Intel's various new 3D chip packaging technologies on the anvil.
2021 will see the introduction and ramp-up of the N5P node, an enhancement of the 5 nm N5 node, offering a 10% improvement in power at the same performance, or 5% increase in performance at the same power. A nodelet of the N5 family of nodes, called N4, could see risk production in Q4 2021. The N4 node is advertised as "4 nm," although the company didn't get into its iso-power/iso-performance specifics over the N5 node. The next major node for TSMC will be the 3 nm N3 node, with massive 25%-30% improvement in power at the same performance, or 10%-15% improvement in performance at same power, compared to N5. It also offers a 70% logic density gain over N5. 3DFabric technology is a new umbrella term for TSMC's CoWoS (chip on wafer on substrate), CoW (chip on wafer), and WoW (wafer on wafer) 3-D packaging innovations, with which it plans to offer packaging innovations that compete with Intel's various new 3D chip packaging technologies on the anvil.