Intel to Keep Its Number One Semiconductor Supplier Ranking in 2020: IC Insights
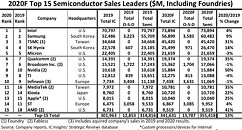
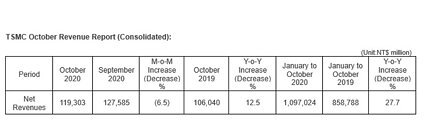
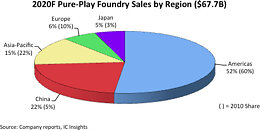
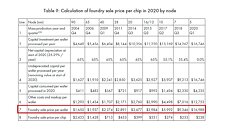
IC Insights' November Update to the 2020 McClean Report, released later this month, includes a discussion of the forecasted top-25 semiconductor suppliers in 2020. This research bulletin covers the expected top-15 2020 semiconductor suppliers (Figure 1).
The November Update also includes a detailed five-year forecast through 2024 of the IC market by product type (including dollar volume, unit shipments, and average selling price) and a forecast of the major semiconductor industry capital spenders for 2020. A five-year outlook for total semiconductor industry capital spending is also provided.
The November Update also includes a detailed five-year forecast through 2024 of the IC market by product type (including dollar volume, unit shipments, and average selling price) and a forecast of the major semiconductor industry capital spenders for 2020. A five-year outlook for total semiconductor industry capital spending is also provided.