Intel CEO Says Using Competitor's Semiconductor Process in Intel Fabs is an Option
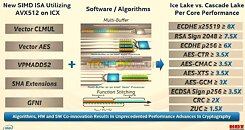
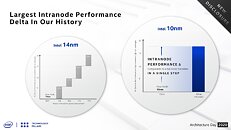
Semiconductor manufacturing is not an easy feat to achieve. Especially if you are constantly chasing the smaller and smaller node. Intel knows this the best. The company has had a smooth transition from other nodes to the smaller ones until the 10 nm node came up. It has brought Intel years of additional delay and tons of cost improving the yields of a node that was seeming broken. Yesterday the company announced the new Tiger Lake-H processors for laptops that are built using the 10 nm process, however, we are questioning whatever Intel can keep up with the semiconductor industry and deliver the newest nodes on time, and with ease. During an interview with Intel's CEO Bob Swan, we can get a glimpse of Intel's plans for the future of semiconductors at the company.
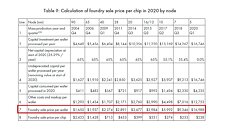
In the interview, Mr. Swan has spoken about the technical side of Intel and how the company plans to utilize its Fabs. The first question everyone was wondering was about the state of 10 nm. The node is doing well as three Fabs are ramping up capacity every day, and more products are expected to arrive on that node. Mr. Swan has also talked about outsourcing chip production, to which he responded by outlining the advantage Intel has with its Fabs. He said that outsourcing is what is giving us shortages like AMD and NVIDIA experience, and Intel had much less problems. Additionally, Mr. Swan was asked about the feasibility of new node development. To that, he responded that there is a possibility that Intel could license its competitor's node and produce it in their Fabs.
In the interview, Mr. Swan has spoken about the technical side of Intel and how the company plans to utilize its Fabs. The first question everyone was wondering was about the state of 10 nm. The node is doing well as three Fabs are ramping up capacity every day, and more products are expected to arrive on that node. Mr. Swan has also talked about outsourcing chip production, to which he responded by outlining the advantage Intel has with its Fabs. He said that outsourcing is what is giving us shortages like AMD and NVIDIA experience, and Intel had much less problems. Additionally, Mr. Swan was asked about the feasibility of new node development. To that, he responded that there is a possibility that Intel could license its competitor's node and produce it in their Fabs.