Cincoze Announces Flagship GP-3000 Industrial-Grade High-Performance GPU Computer
Cincoze, a professional manufacturer of embedded systems, has announced its new flagship GPU edge computing system, the GP-3000. Its crowning feature is an exclusive GPU Expansion Box that provides expansion for up to two high-end GPU graphics cards and creating a high-performance industrial-grade GPU computer. Brandon Chien, General Manager of Cincoze, stated that "We already know AI will drive innovation and expansion for industrial applications. The GP-3000 is Cincoze's answer for intensive image processing and complex calculations, such as deep machine learning, autonomous driving, automated visual inspection, and mobile monitoring. As our latest flagship model, the GP-3000 multiplies edge computing efficiency, amplifies productivity and reliability, and accelerates AIoT automation."
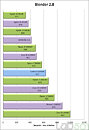
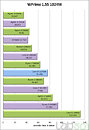
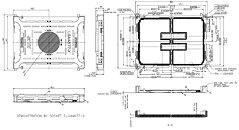
The GP-3000's extreme computing power starts with an 8th or 9th generation Intel Xeon or Core i3/i5/i7 (Coffee Lake and Coffee Lake-R) CPU, Intel C246 chipset, and supports two sets of DDR4-2666 ECC/non-ECC SO-DIMM up to 64 GB and can support up to two 250 W high-end GPU graphics cards. With a total system power consumption of 720 W, it's easy to meet and exceed high-efficiency application requirements. A precision heat dissipation and cooling design quickly wick away heat, keeping the focus squarely on the breathtaking performance of the GP-3000.
The GP-3000's extreme computing power starts with an 8th or 9th generation Intel Xeon or Core i3/i5/i7 (Coffee Lake and Coffee Lake-R) CPU, Intel C246 chipset, and supports two sets of DDR4-2666 ECC/non-ECC SO-DIMM up to 64 GB and can support up to two 250 W high-end GPU graphics cards. With a total system power consumption of 720 W, it's easy to meet and exceed high-efficiency application requirements. A precision heat dissipation and cooling design quickly wick away heat, keeping the focus squarely on the breathtaking performance of the GP-3000.