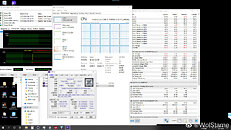
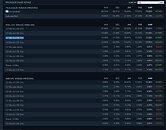
Intel Core i7-1185G7 "Tiger Lake" Ships with 4.70 GHz Turbo Boost Speeds
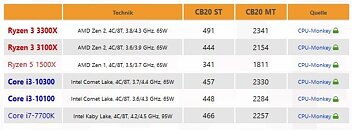
Intel spoke of a "double digit percentage performance growth generation on generation" at its product reveal for "Tiger Lake" along the sidelines of its CES event. We now have a theory as to how they arrived at that. The company's 11th generation Core "Tiger Lake" processor, scheduled to launch sometime mid-2020, could bring about big gains in per-core performance for the ultraportable segment. PC enthusiast MebiuW, who has had a high hit-rate with Intel leaks, revealed that the flagship "Tiger Lake" part, the Core i7-1185G7, could ship with a CPU Turbo Boost speed of 4.70 GHz, a steep increase from the 3.90 GHz of the top current "Ice Lake" part, the i7-1065G7. The increased clock speeds, coupled with the more advanced "Willow Cove" CPU cores appear to be the 11th generation chip's value proposition.